Phone No: 866 806 2227 / 240 660 0276 || Email: [email protected] || Address: 157 church street New haven CT 06510
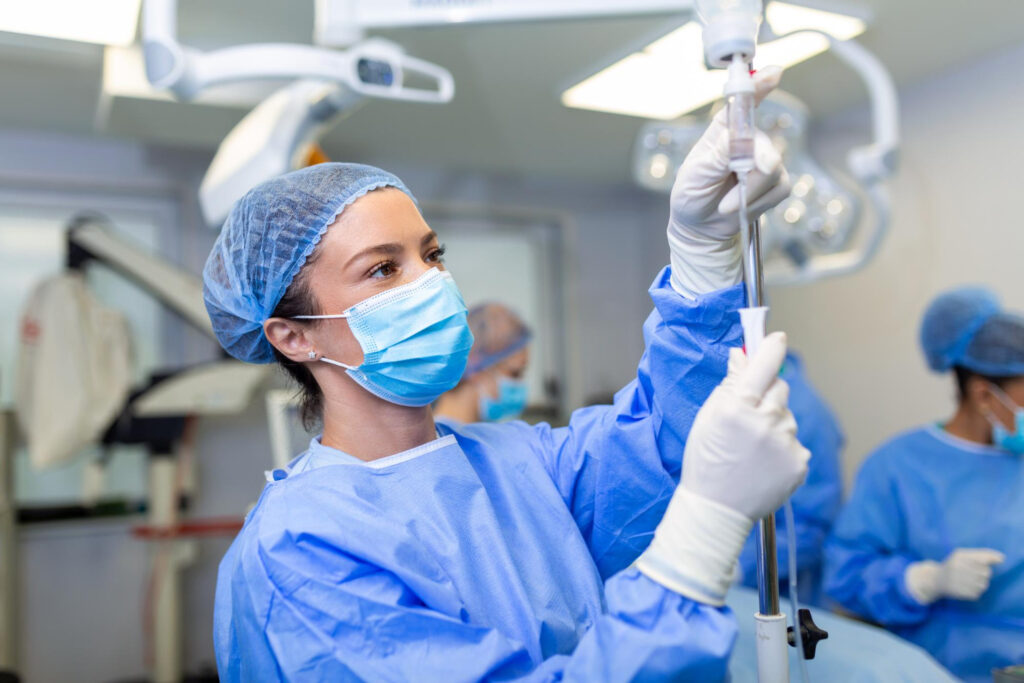

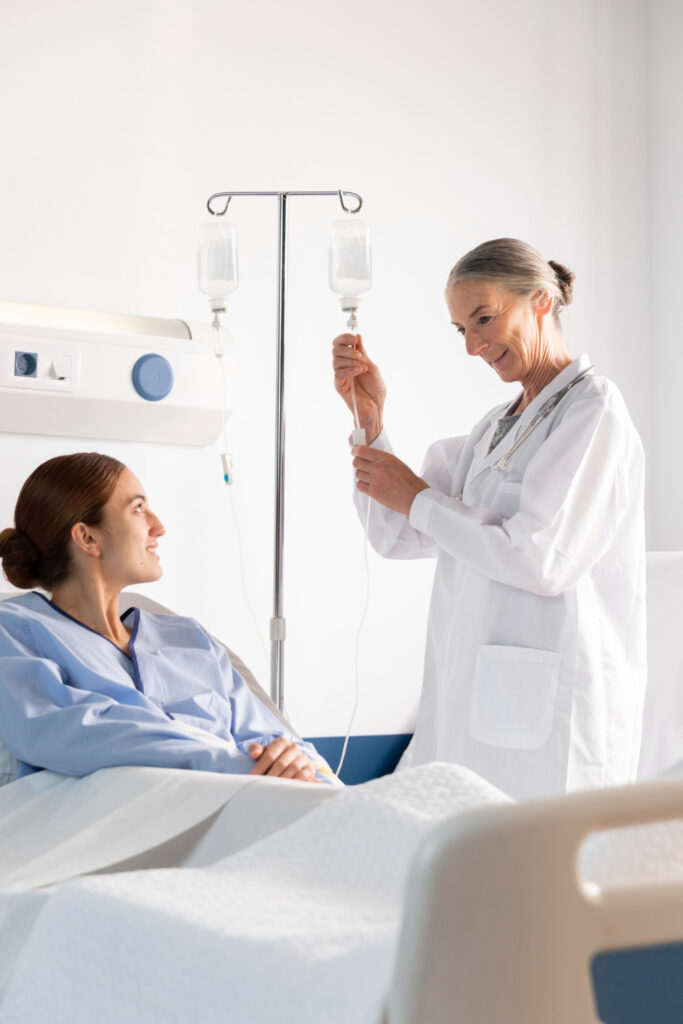
Intravenous therapy, commonly referred to as IV therapy, is a medical procedure that involves the administration of fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the veins. It is a widely used method for delivering various substances into the bloodstream, providing rapid and efficient absorption.
Intravenous therapy plays a crucial role in medical settings, ranging from hospitals and clinics to emergency rooms and ambulatory care centers. This article will explore the benefits, procedure, and considerations associated with intravenous therapy.